Describe the Structure of Atp and How It Stores Energy
A catalyzes metabolic reactions b storage of energy c transfer information for protein synthesis d long-term. The small structures in cells that carry out this energy-storing process are known as mitochondria.
A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism and all living structures in the human body are made of cells.
. A muscle fi bre stores only a small amount of ATP so the force and duration of a muscular effort is only as effective as the ATP replenishment process. The main reason that ATP is considered the energy currency in cells is because it. The formula for photosynthesis is Suns.
The formula for cellular respiration is C. In smooth muscle. The boundary of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope.
C Contraction in smooth muscle. Energy for muscular activity. These energy needs are met through mitochondria myoglobins and rich blood supply from the coronary arteries.
The drawing shows some of the structures present in G. The anaerobic glycolysis system for intermediate bursts of relatively high intensity this system produces the by-products of lactate ions and hydrogen ions commonly known as lactic acid. ATP is the universal and most important intermediate of cellular energy transactions and in addition is a ubiquitous extracellular messenger involved in many pathophysiological responses 1.
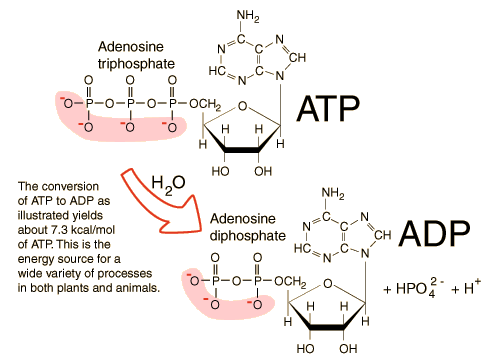
They are membrane-bound vesicles formed in the Golgi apparatus. It is caused by the microorganism Giardia lamblia. O energyATP Plants carry out photosynthesis for the production of glucose.
Energy demands of Football. Surprisingly in 1974 Dowdall 79 and co-workers found a considerable amount of ATP together with acetylcholine in cholinergic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. A eukaryotic cell consists of several membrane-bound structures in its cytoplasm.
Identify the structure and function of cytoplasmic organelles. Describe how the structure of a cholera bacterium is different. SO 253 Describe the structure and functions of deoxyribonucleic acid DNA ribonucleic acid RNA and adenosine triphosphate ATP.
They produce energy ATP and therefore are called the powerhouse of the cell. Exercise activity number of calories required to sustain life without movement or physical activity bmr basal metabolic rate _____ is the smallest daily contributor to energy expenditure but an important indicator or weight loss non exercise activity thermogensis there is a direct mathematical relationship between the amount of _____ we breathe in and the amount of. Hence ATP cannot be stored easily within cells and the storage of carbon sources for ATP production such as triglycerides or glycogen is the best choice for energy maintenance.
Describe the structure and functions of the plasma cell membrane. Explain how this is an adaptation to living in the intestines. The nuclear membrane is continuous with the.
When a cell uses substantial energy to organize its cell contents to a greater degree than the organization that exists outside the living cell entropy has decreased. The rest of the chemical energy of O 2 and the carbohydrate or fat are converted into heat. 2 ATP then binds to myosin.
Contains accessible energy in phosphate bonds. By structure it is a porous membrane with pores which permit the movement of selective substances in and out of the cell. Energy is necessary for all metabolic activity within the cell.
Short for adenosine triphosphate. Glycogen synthase deficiency also. Cells use oxygen and simple sugars to create this molecule the main source of their energy.
Describe the energy requirements of cardiac muscle tissue. D adds a phosphate group. During and after physical exertion the body uses several methods of recovery to rebuild used supplies of ATP and food fuels.
Lysosomes are also called. A small structure in cells that performs a specific function comes from another cell directs the activities of a cell thick fluid between the nucleus and the cell membrane carries out the functions of life surrounds lysosomes vacuoles and other cell parts stores DNA can make a copy of itself a ribosome is one of these Homework. A Flagellum Sucker Nucleus Ribosomes Name one.
It forms the wall-like structure between two cells as well as between the cell and its surroundings. E is highly reversible. Key Takeaways Key Points.
The word eukaryotic cell is used to describe the structure of a general eukaryotic cell. 6 ADP is then released. A mnemonic is a device such as a pattern of letters.
Mitochondria possess their own DNA RNA and components required for protein synthesis. In eukaryotic cells. 4 A cross-bridge forms and myosin binds to a new position on actin.
In this article we will discuss the general structure of a eukaryotic cell as well as the differences found in the cells of the four kingdoms of eukaryotes. Can use to create ATP. The nucleus stores chromatin DNA plus proteins in a gel-like substance called the nucleoplasm.
The nucleolus is a condensed region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis occurs. An outer membrane and an inner membrane. Just to remind you there are three major systems available for the production of energy in the muscles.
The glucose then becomes the energy source for cellular respiration. B requires the input of energy. The myocardium requires significant energy to contract continually over the human lifetime.
Cells make this molecule to power almost all of their activities. Lamblia can attach itself with its sucker. Describe the nucleus and its function.
Sec 25 Organic Compounds 44 Which of the following is the major function of DNA. The deficiency of glycogenin-1 leads to lack of glycogen energy stores and is accompanied by metabolic abnormalities as discussed in this case. C stores energy in the release of an inorganic phosphate group.
The cytoplasm of the cell is. The ATP-PC system for high-intensity short bursts. Besides this the cell membrane also protects the cellular component from damage and leakage.
Like a battery ATP stores a bit of usable. The mitochondria generate ATP for the contraction of cardiomyocytes. 5 Pi is released and myosin changes conformation resulting in the power stroke that causes the filaments to slide past each other.
It should be emphasized that despite the fact that cardiac muscle is capable of the oxidation of fatty acids as an energy source glucose is an important energy source to meet its metabolic demands. Helps in regulating cell metabolism. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body which vary in.
The conversion of ATP into ADP a is an example of a exchange reaction. 3 ATP is then hydrolyzed. It consists of two phospholipid bilayers.
The ATP is used as a sort of energy currency and some of the chemical energy it contains is used for other metabolism when ATP reacts with OH groups and eventually splits into ADP and phosphate at each stage of a metabolic pathway some chemical energy is converted into heat. The high energy bond in ATP is found in or between. L mark Giardiasis is an intestinal disease.

Where Is The Energy Stored In Atp Molecules Socratic

Comments
Post a Comment